Retail & Wholesale Companies using SAP ERP can easily leverage their existing SAP solutions to provide customers with additional checkout and payment options to their customers. These options can be enabled using existing modules in the ERP solution, such as Loans Management (CML), Collateral Management (CMS), and Bank Customer Accounts (BCA). With these modules, any company can start offering different payment options such as Buy-Now-Pay-Later (BNPL) and financed purchases, as well as lending directly through collateralized Lines of Credit and other liquidity-focused loans. Considering SAP is a multi-company system, the same functionality can be provided by corporates directly and by Captive Finance subsidiaries.
The Starting Point
As of today, more than 160,000 companies in North America leverage SAP software to run their businesses. Most of them own an ERP solution, such as the SAP ECC or S/4 HANA applications. In order to run their businesses, they activate features and processes in each of the different modules. For example, a company that requires management over their sales and delivery of products can activate the Sales & Distribution module (SD), if they want to manage their procurement and purchasing process to then manage the inventory of purchased goods, they can activate the Materials Management module (MM).
However, the result of a Sales Order or a Purchase Order in the SAP system is usually an Invoice that creates an Account Receivable (FI-AR) or an Account Payable (FI-AP). Both items would be posted into a Customer/Vendor sub-ledger (as well as to General Ledger) with a payment term such as NET30, NET60, or NET90. By default, the SD and FI-AR modules cannot provide customers with financing options such as paying in installments with interest, BNPL, or withdrawing funds from a pre-approved Line of Credit. Nonetheless, SAP Fioneer offers a solution within SAP ECC and SAP S/4 HANA to deal with this scenario.
Providing BNPL and Financing Options with SAP Loans Management (CML)
SAP Loans Management (formerly CML) is a sub-ledger solution within S/4 HANA and SAP ECC that integrates with FI-AR to create, manage, and bill for loan contracts of different types. SAP Loans Management is a complete loan servicing solution, and it is currently leveraged by banks and financial institutions around the world. Some Retail and Wholesale companies in North America are also leveraging SAP Loans Management to provide financing options to their customers, either by integrating with the SD module or by simply taking the loan that is created through a sales channel at the moment of purchase.
There are many ways in which Retail and Wholesale companies decide to leverage the Loans Management solution, the most natural is to work out an integration with the SD module, so that whenever the Sales Order is delivered and the invoice created, it is also internally cleared by an SAP CML loan disbursement, and thus no cash would be received or delivered by both parties at the moment of purchase. In other words, the sale made is automatically paid for by the loan proceeds of the same customer, and at the same time, the customer can repay its new loan following a planned amortization table with more attractive financial conditions.
Now, given that the Loans Management (CML) module is flexible enough to model any type of amortization table by using a descriptive mechanism based on financial conditions, it is possible to enable any type of financing option known in the market.
Here are a few of the loan product types that have been implemented over the years in customers owning SAP ERP solutions:
-
Buy Now Pay Later
-
Installment Plans
-
Employee Loans
-
Collateralized Lending
-
Commercial Lines of Credit
-
Receivable Financing and Factoring (We will save this one for a future blog)
Buy Now Pay Later
Business Scenario: B2B / B2C
Loan Scenario: Loan Given
Description: During the checkout of the Customer Purchase, the user can select the BNPL payment option. Once the products are delivered and the invoice generated, the loan contract can be created automatically through BAPIs (Business APIs) and leveraging the extensibility of the standard SD Module through BADIs (Business Add-In). In this case, the loan contract amount matches the invoice amount, the loan contract term matches the invoice term, and there is (usually) no interest rate.
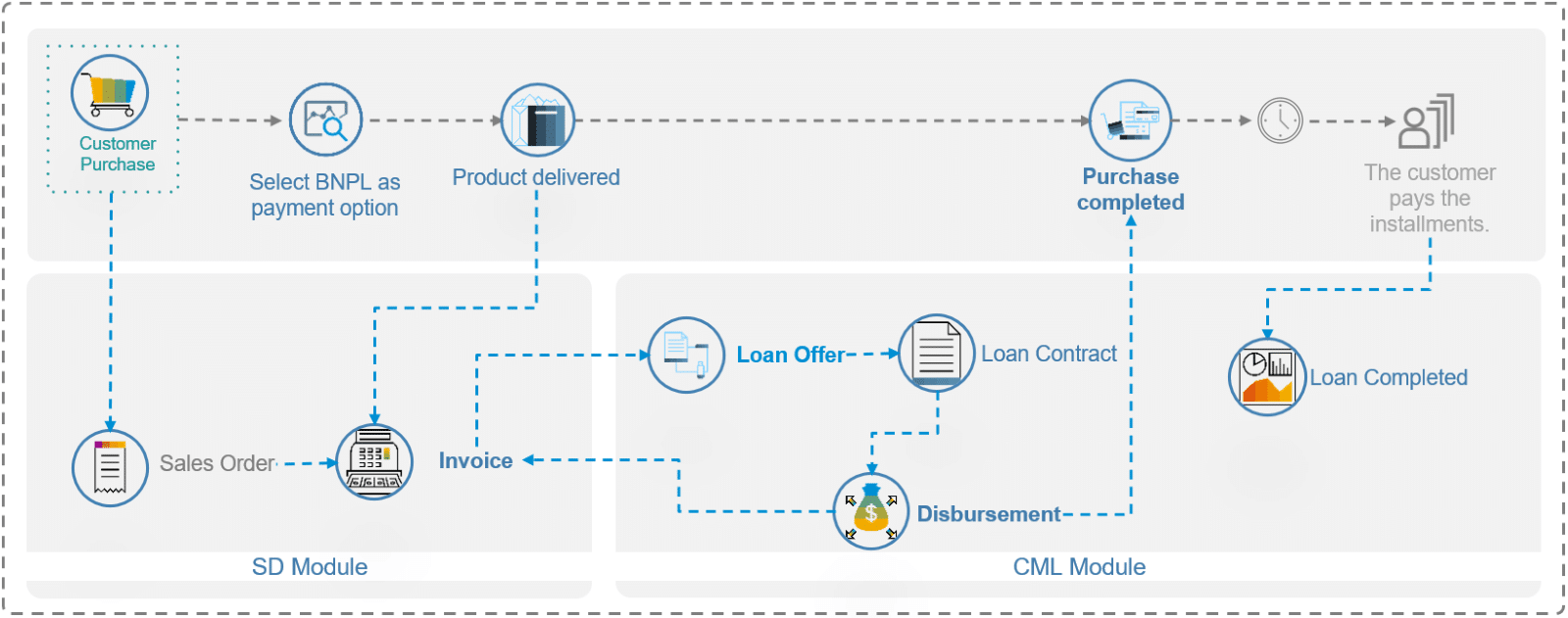
Alternatively, the Loan Contracts can be created in a different Company Code, which would be needed if the retailer/wholesaler has set up a Captive Finance company to account for the lending services.
Installment Plans
Business Scenario: B2B / B2C
Loan Scenario: Loan Given
Description: During the checkout of the Customer Purchase, the user can select the “Pay in Installments” option. Once the products are delivered and the invoice generated, the loan contract can be created automatically through BAPIs (Business APIs) and leveraging the extensibility of the standard SD Module through BADIs (Business Add-In), in the same way as the BNPL option. In this case, the business would be providing the customer with a longer period to repay (e.g., 12 months instead of 30 days) with interest payments. Since this is a riskier arrangement, a down payment can be expected and the financed amount would be less than the invoice amount.
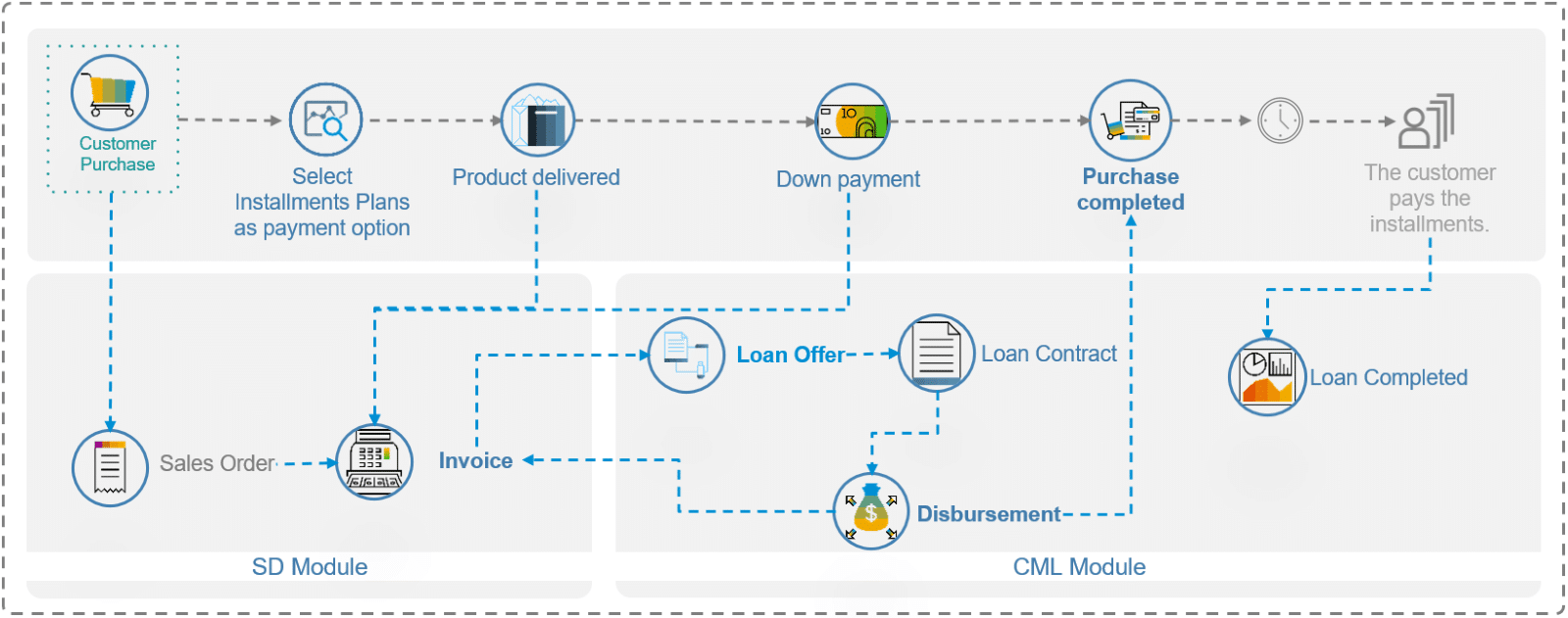
Similarly to the BNPL payment option, the Loan Contracts can be created in a different Company Code, which would be needed if the retailer/wholesaler has set up a Captive Finance company to account for the lending services.
Employee Loans
Business Scenario: B2E
Loan Scenario: Loan Given
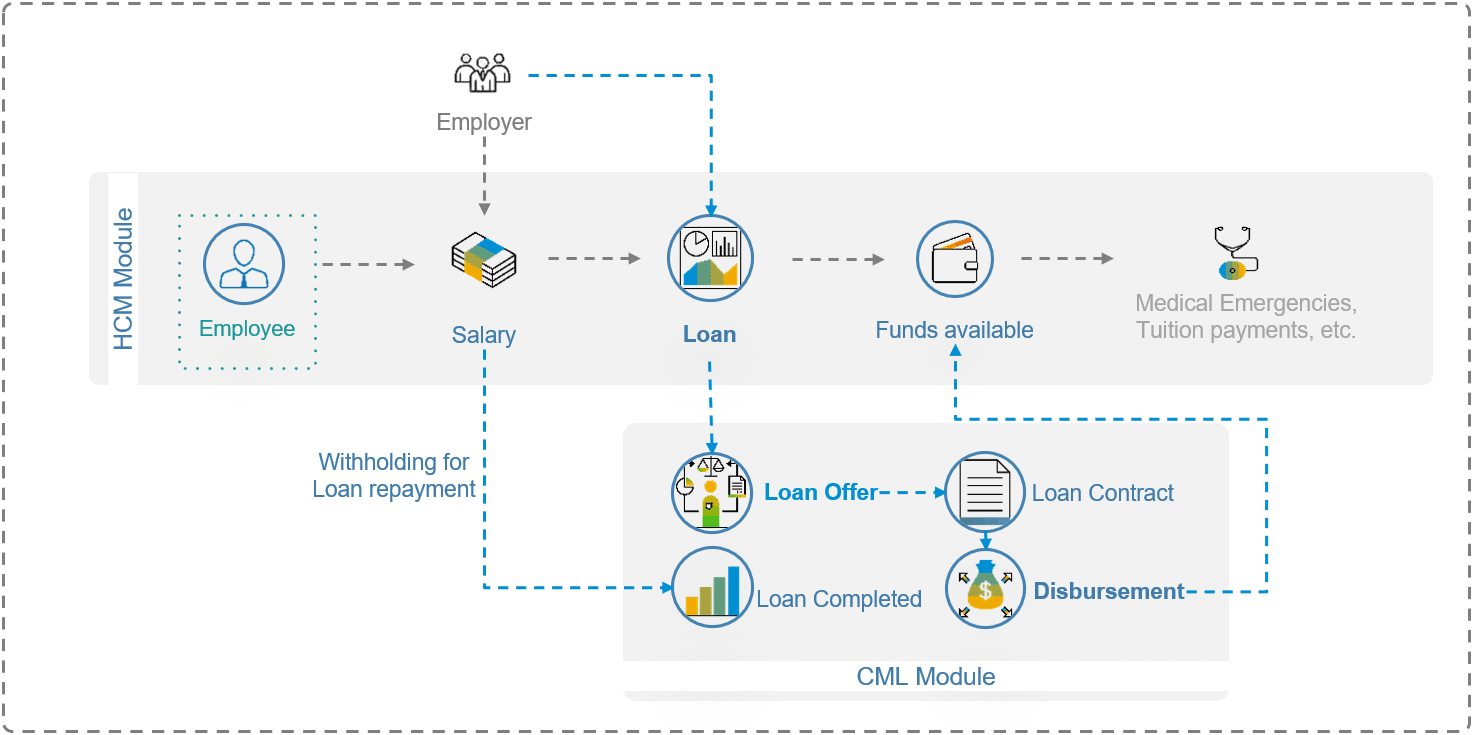
Description: In a Business to Employee scenario, the business will offer its employees loans against their salary income. The disbursement of the loan can be paid by the SAP HCM module, and the payments to the loan can be withheld from the salary paid in HCM as well. The loan management and servicing can be done in SAP CML, and the loan contract can be created automatically through BAPIs (Business APIs) and integrated through HCM BADIs (Business Add-In).
Collateralized Lending
Business Scenario: B2B
Loan Scenario: Loan Given
Description: Collateralized lending happens anytime the borrower provides an asset as collateral for their loan. Usually, banks are in the business of collateralized lending through an array of financial products for both customers (B2C) and SMEs (B2B), but companies in the supply chain are often better positioned to offer financial services that augment the value added or increase the efficiency of their own supply chain. For example, any corporation can offer collateralized lending to their retailers, just by registering the retailer’s assets or inventory as collateral.
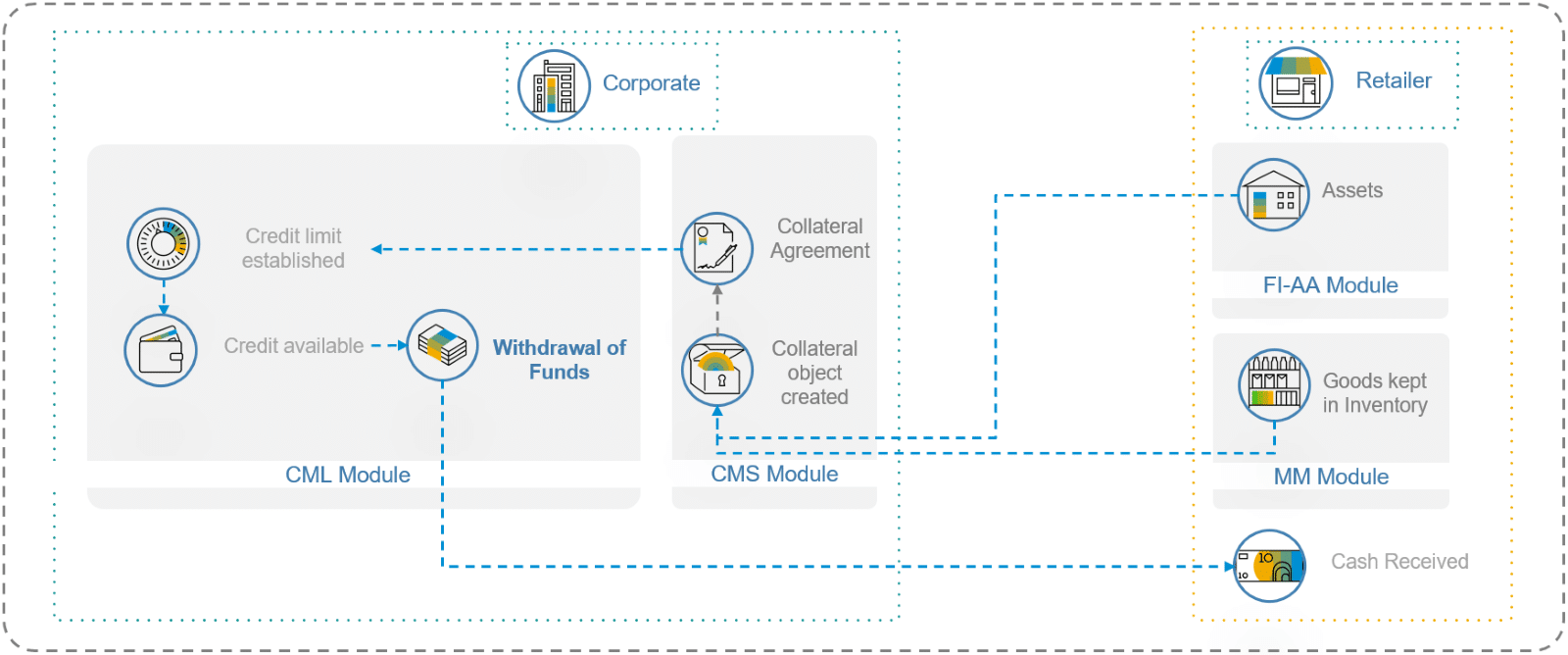
A variation of the above is when the corporate offers collateralized lending with special conditions for collaterals that are goods sold by the corporate itself. While these goods are kept in the inventory of the retailer, they can leverage them as collateral to get liquidity against them, both parties benefit as this inventory is valuable for both parties, as compared to the value that the same inventory would have in any other bank.
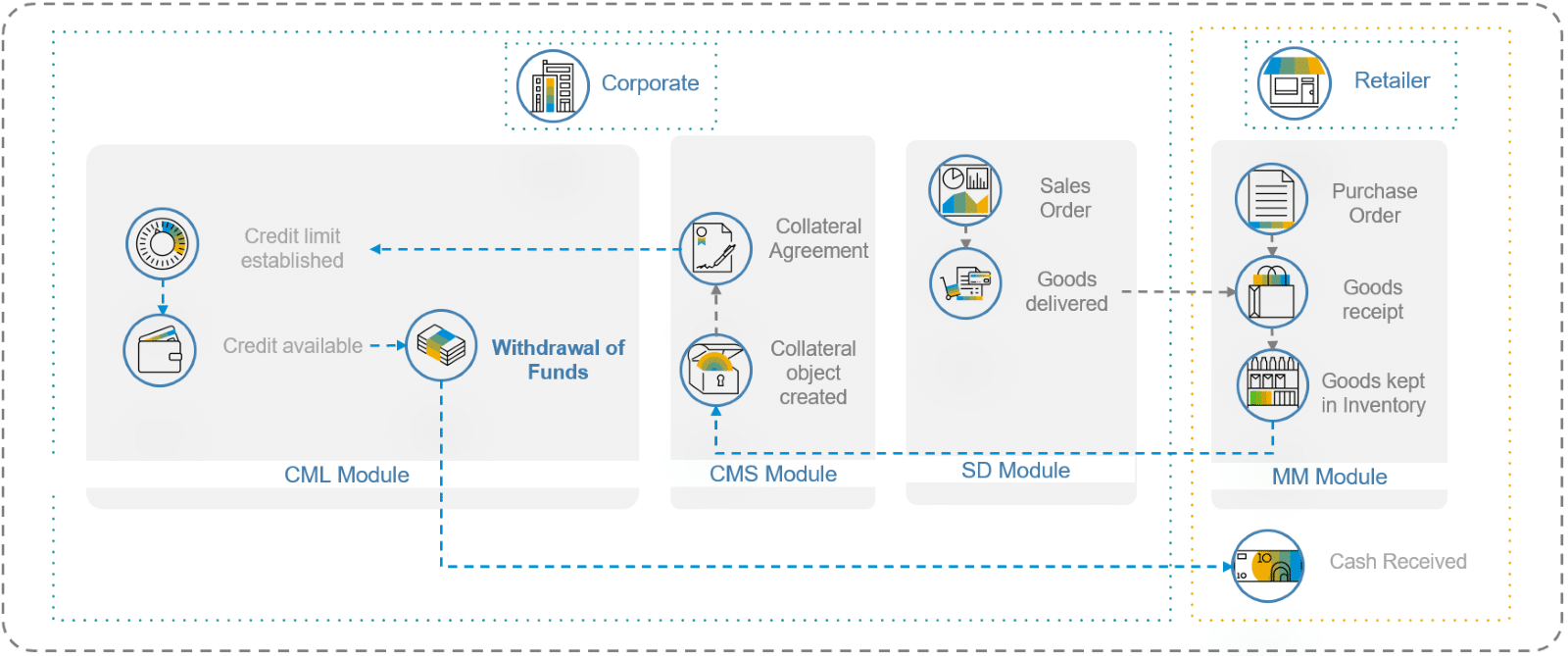
Commercial Lines of Credit
Business Scenario: B2B
Loan Scenario: Loan Taken / Loan Given
Description: Financing is as important for sales as it is for purchases. Retailers buying goods from a wholesaler, or wholesalers buying raw materials (using SAP MM) will normally look for working capital in the form of debt. For this, a loan or a revolving line of credit must be acquired from an external financial institution. During the requisition process, an Account Payable Invoice will be created, and the business can choose to finance this payment by withdrawing from the pre-approved line of credit. Furthermore, the system can be configured and enhanced to repay this credit line whenever cashflows are realized from the sales of the products.
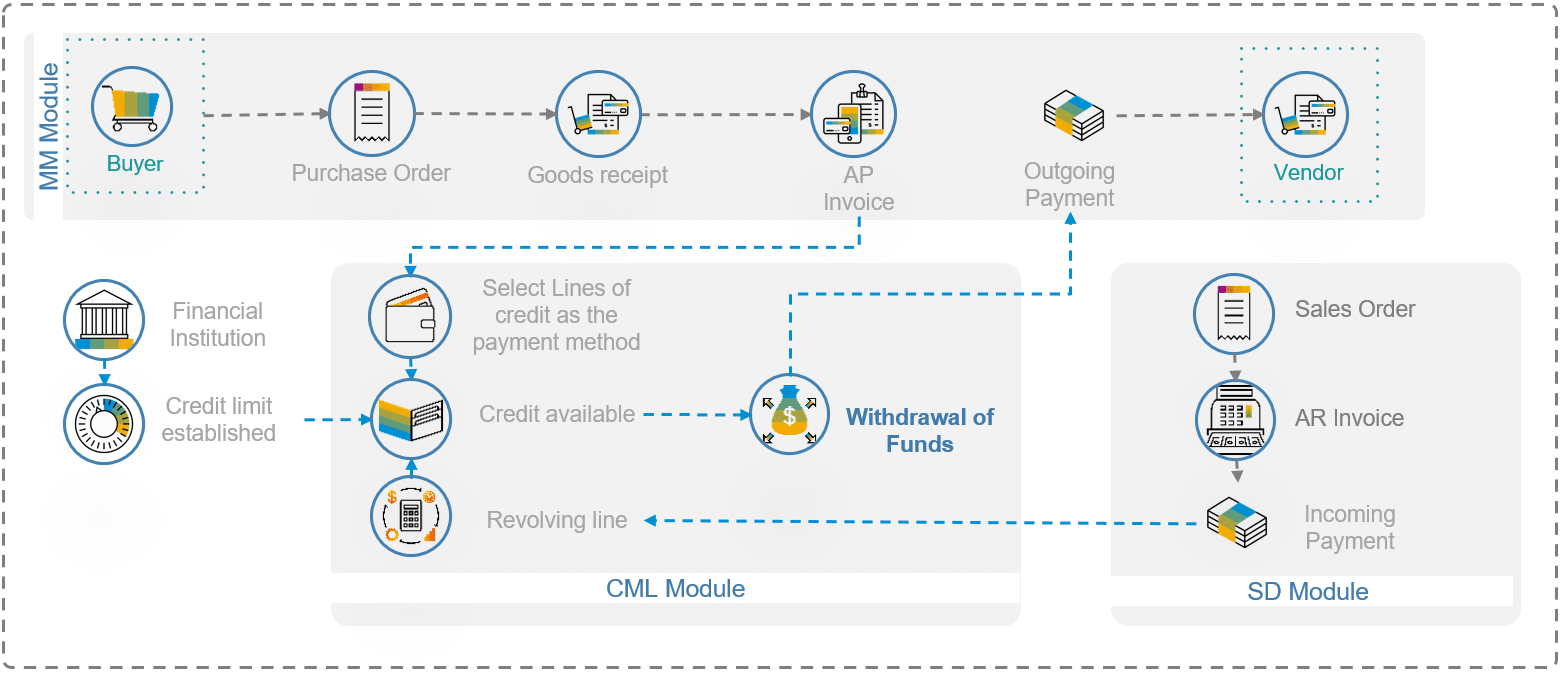
Corporates can choose to manage commercial loans taken as well as commercial loans given, in a similar manner to the Collateralized Lines of Credit.
