SAP S/4HANA is SAP’s current enterprise application suite. Originally released in June 2014 as a next-generation financial solution under the name SAP Simple Finance, it only took SAP nine months to announced that it was expanding the core of the solution to become a full-scale enterprise resource planning platform, and renamed the suite SAP S/4HANA, with specific core lines of business tacked on to the end of the suite name.
In 2016, logistics functionality was introduced to SAP S/4HANA in four key areas:
- Sourcing and procurement
- Manufacturing
- Supply chain
- Asset management
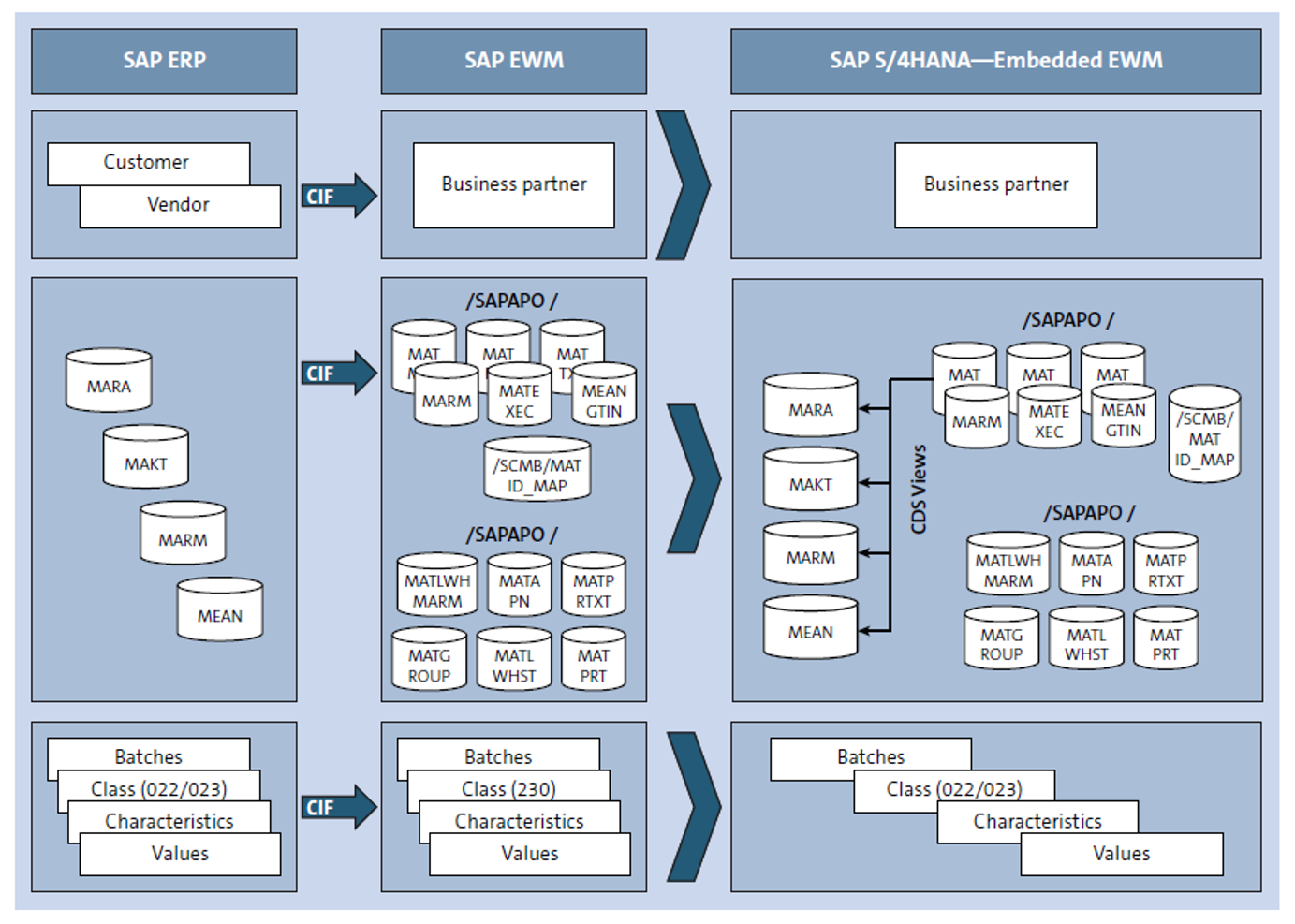
Major enhancements over SAP ERP included embedding extended warehouse management (EWM) and production planning/detailed scheduling (PP-DS) functionality directly into SAP S/4HANA.
SAP added machine learning capabilities to the suite in 2017 in order to perform easier goods and invoice receipt reconciliation and to automate invoice assignments. In September of that year, transportation management functionality was embedded in SAP S/4HANA. In 2018, predictive accounting functionality was added, and subsequent releases of the solution included additional intelligent technology enhancements in the areas of artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things.
As of 2021, an embedded human resources line of business is in development, and SAP has released multiple industry-specific offerings of SAP S/4HANA: energy and natural resources, service industries, consumer industries, discrete industries, financial services, and public services.
SAP S/4HANA Finance
The SAP S/4HANA Finance LoB focuses on all money-related activities of a business. This includes financial accounting, controlling, treasury and risk management, financial planning, financial close, and consolidation.
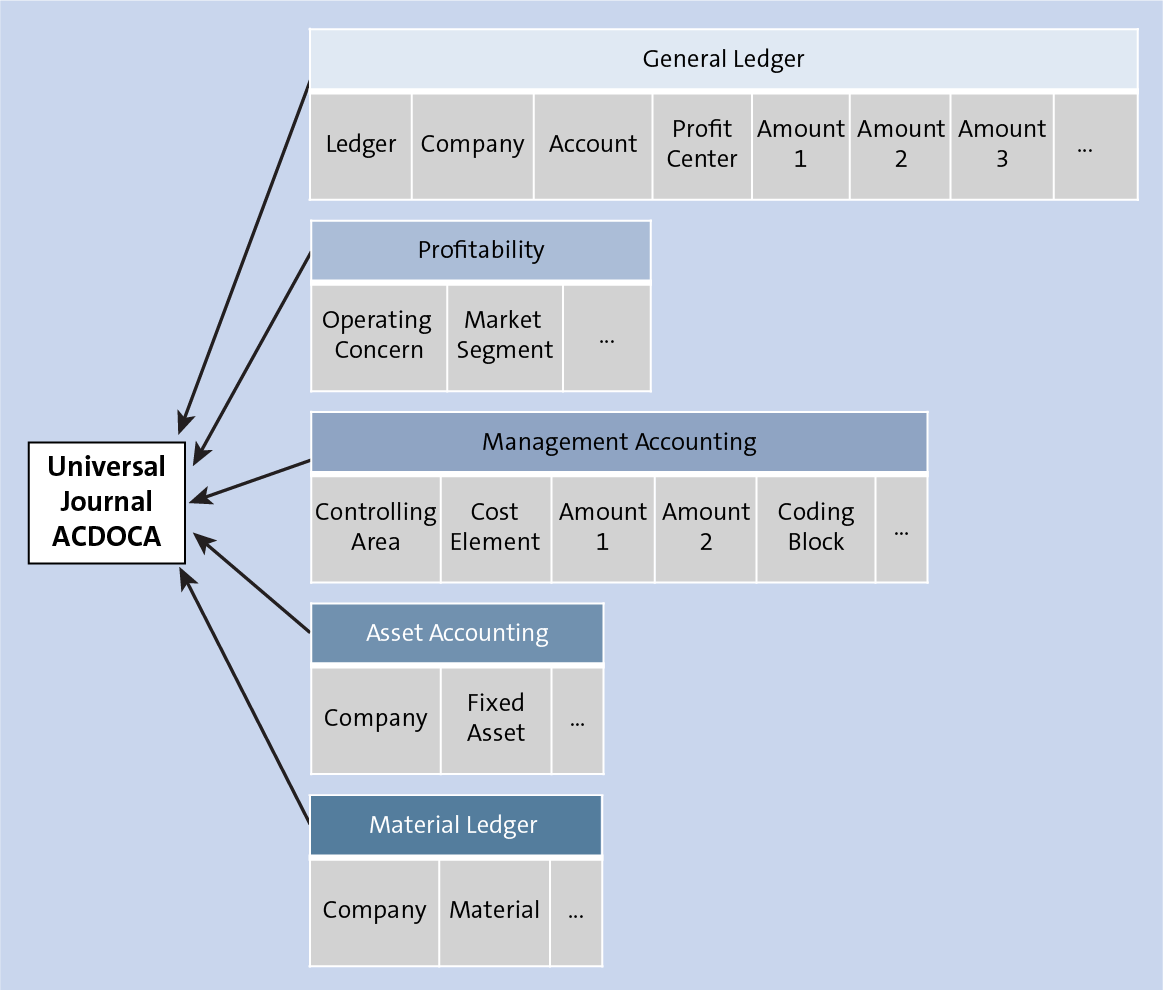
Central to the SAP S/4HANA Finance solution’s unique selling proposition are the process and reporting improvements available thanks to SAP HANA. While some of these were just processing speed upgrades—the SAP HANA database boasts analytics and reporting capabilities that are 1800x faster than SAP ERP—many were brand-new to SAP S/4HANA Finance. This includes things like the Universal Journal, centralized processing, data drilldown, and ability to integrate multiple ERPs into one place for data collection.
SAP was clear from the beginning that the “simple” in SAP S/4HANA Finance’s first iteration was multifaceted. Those using the new solution would find not only automatic, up-to-the-minute financial reporting, but a streamlined data model and lightweight architecture.
Initial FI-CO functionality improved upon the existing ERP. This included updated financial planning and analysis, accounting and financial close, treasury and financial risk management, collaborative finance operations, and enterprise risk and compliance management.
SAP S/4HANA Finance introduced to the financial world the tangibility of a single source of truth—that is, an aggregated total of all financial data across departments, ledgers, and even continents. This was enabled by SAP HANA’s ability to store large amounts of data in-memory and to produce analytics reports at a moment’s notice for anyone with access who wanted it. This provided immediate value to accountants looking at current and past activity, project managers running complex projects on tight budgets, and planners looking to utilize past and present numbers to forecast future expectations.
Contact us to implement SAP S/4HANA in your company.






